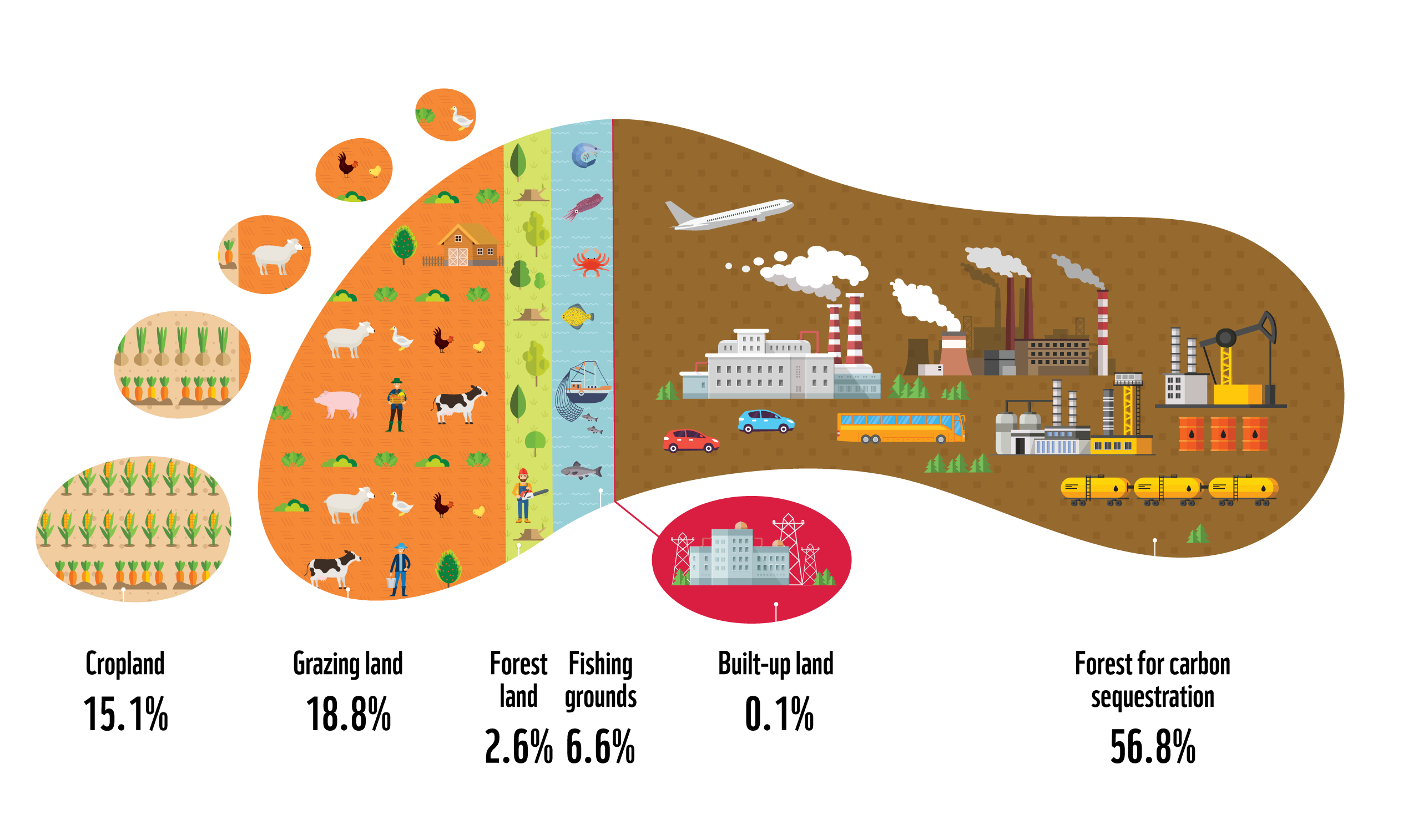
Development of Ecological Footprint Biology Diagrams Background Revealing motivations in food choice and investigating the potential role of sustainable healthy eating behavior, ecological footprint awareness and food security in food choice are important points for a sustainable life. This study was conducted with 5285 adults aged 19-65 residing in Turkey to investigate their food choice motivations in terms of sustainable and healthy eating The prevailing ecological deficit is devastating the ecosystem which is leading toward the unsustainability by endangering the livings on earth. The important drivers of this environment degradation are natural resources depletion, financial development and the economic growth which are investigated to test their impact on ecological footprints. The EKC hypothesis is evaluated to test the Food supply has been the central issue of human development for millennia and has become increasingly critical in an urbanizing world. However, the environmental footprints and associated mitigation strategies of food consumption have rarely been comprehensively characterized at urban or regional scales. Here, we analyze the water, carbon, reactive nitrogen, and phosphorus footprints of food
The ecological footprint considers the pressure on ecosystems resulting from human activities, the land footprint quantifies land occupation, the energy footprint measures energy consumption, and the biodiversity footprint focuses on the impact on biodiversity FLW is prevalent throughout various stages of the food supply chain, contributing agri-enterprises to viable markets; high levels of food loss and waste; increased incidences of food safety, and animal and human health issues; and an increased energy-intensity and ecological footprint associated with the lengthening and industrialization of food supply chains.

Determining food choice motivations in Turkish adults: sustainable and ... Biology Diagrams
Human diets have enormous implications for both human and environmental health 1,2,3,4,5,6.The global food system is fuelled by extensive appropriation and degradation of Earth's natural capital

1. Introduction. Food is a basic need for humans but the way in which much of it is produced, distributed, and consumed, is not sustainable. Challenges include among other things, biodiversity loss, climate change, environmental degradation, diet-related diseases, and unequal access to food (Schneider et al., Citation 2023).A 'food system' perspective helps to better understand the root Food and life cycle energy inputs: consequences of diet and ways to increase efficiency. Ecological Economics, 44(2-3), 293-307. 'Food miles' are measured in tonne-kilometers, representing the transport of one tonne of goods by a given transport mode (road, rail, air, sea, inland waterways, pipeline, etc.) over a distance of one kilometer.